User Guide
ContaX is a desktop application for managing your Contacts and Schedule. It is a powerful tool optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI), while incorporating Graphical User Interface (GUI) elements to make it user-friendly. If you are able to type fast, ContaX is capable of helping you manage your contacts and schedule more efficiently than traditional GUI applications, enabling you to shift your focus to other more important things.
Broadly speaking, ContaX consists of an Address Book for managing Contacts, and a Schedule for managing Appointments.
ContaX is designed with versatility in mind, so it does not place unnecessarily strict constraints on your inputs. It accepts all inputs, even those that remotely have a chance of being valid. For more details, see the Global Input Constraints section.
- Quick start
- Global Input Constraints
-
Features
- Onboarding guide
- Viewing help :
help - Clearing all entries :
clear - Adding a person:
addperson - Listing all persons :
listpersons - Editing a person :
editperson - Locating persons by attribute:
findperson - Deleting a person :
deleteperson - Creating a Tag :
addtag - Editing a Tag :
edittag - Listing All Tags :
listtags - Deleting a Tag :
deletetag - Finding Contacts by Tag :
findbytag - Creating an Appointment :
addappt - Listing All Appointments :
listappt - Deleting an Appointment :
deleteappt - Editing an Appointment :
editappt - Listing Appointments Within A Period :
apptbetween - Listing Empty Slots in Schedule Within A Period :
freebetween - Edit Priority Level of an Appointment :
prioritizeappt - Finding Appointment by Name or Person Name :
findappt - Saving the data
- Exporting the data:
exportcsv - Editing the data file
- Importing data
- Importing CSV Files:
importcsv - Operate on Contacts by Conditional Clause :
batch - Operate on Contacts within Range :
range - Chaining Commands:
chain - Exiting the program :
exit
- FAQ
- Command summary
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
ContaX.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for ContaX.
- Double-click the file to start the app.
 For Users on Mac OSX:
The security policy of OSX might prevent the creation of data files in the same folder. For users on OSX, it is recommended that you
For Users on Mac OSX:
The security policy of OSX might prevent the creation of data files in the same folder. For users on OSX, it is recommended that you
- Navigate to your home folder on Terminal
- Launch the application using the commandjava -jar ContaX.jar.
-
The GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
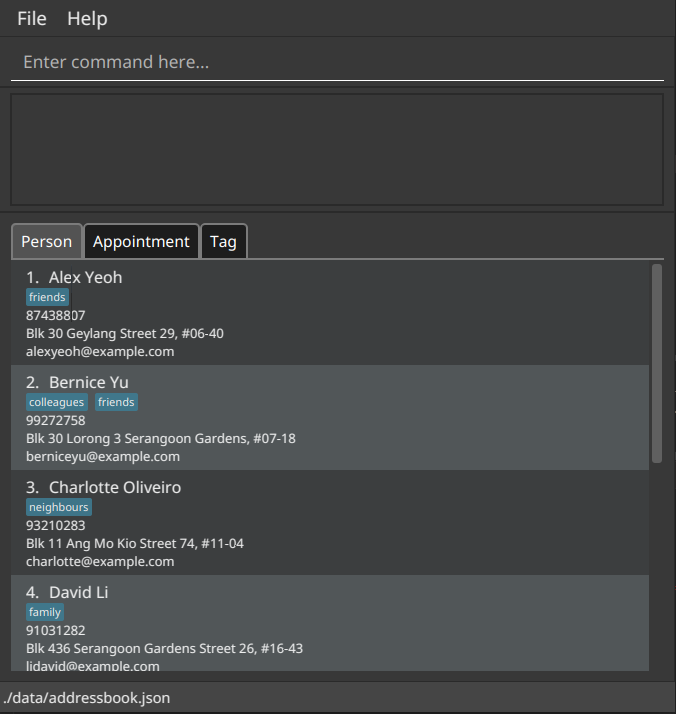
-
If this is your first time running ContaX, you will be prompted to go through an Interactive Onboarding Guide to learn the basics, or you can choose to explore the application by yourself.
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
listpersons: Lists all contacts. -
addpersonn/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01: Adds a contact namedJohn Doeto the Address Book. -
deleteperson3: Deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list. -
clear: Deletes all contacts. -
exit: Exits the app.
-
- Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Global Input Constraints
ContaX is generally designed to impose as little constraints on inputs as possible. However, there still exists certain limitations that apply throughout all features.
-
INTEGER inputs are limited to a maximum value of
2,147,483,647.
Any value above this limit will not be considered an integer. - Leading and Trailing Whitespaces are ignored for ALL user inputs.
e.g.My Tag is treated simply asMy Tag.
Displayed Indexes
The displayed index of a Person, Appointment or Tag refers to the number displayed beside the record in the GUI.
Only positive integers are recognised as a displayed index.
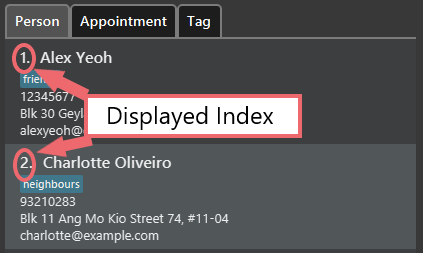
![]() Warning: The displayed index for a record may change with find and list commands. Always check the displayed index before using it in a command.
Warning: The displayed index for a record may change with find and list commands. Always check the displayed index before using it in a command.
Common Date and Time Syntax
![]() Only these format(s) for date and time inputs are allowed.
Only these format(s) for date and time inputs are allowed.
- All date inputs must conform to one of the following formats:
-
dd-mm-yyyyordd/mm/yyyy, or any combination of-and/separators -
dd MMM yyyywith the date components appearing in any order.
If a component appears more than once, the date is considered invalid.
-
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
dd |
Day of the month. |
mm |
Numerical representation of the month, from 1 to 12. |
MMM |
Textual representation of the month, such as oct or october. |
yyyy |
Year in the full 4-digit format. |
- All time inputs must conform to one of the following formats:
- The 24-hour format
hh:mmorhh-mm - The 12-hour format
HH:mm aaorHH-mm aa. The whitespace between the numeric fields andam/pmfield can be omitted.
- The 24-hour format
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
hh |
Hour of the day, in 24-hour format. |
HH |
Hour of the day, in 12-hour format. |
mm |
Minute of the hour, from 00 to 59. |
aa |
Either am or pm, case-insensitive. |
Features
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe.
See the Global Input Constraints section for restrictions on the parameter supplied. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used ast/friend,t/friend t/familyetc. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyp/12341234 p/56785678, onlyp/56785678will be taken. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.
Onboarding guide
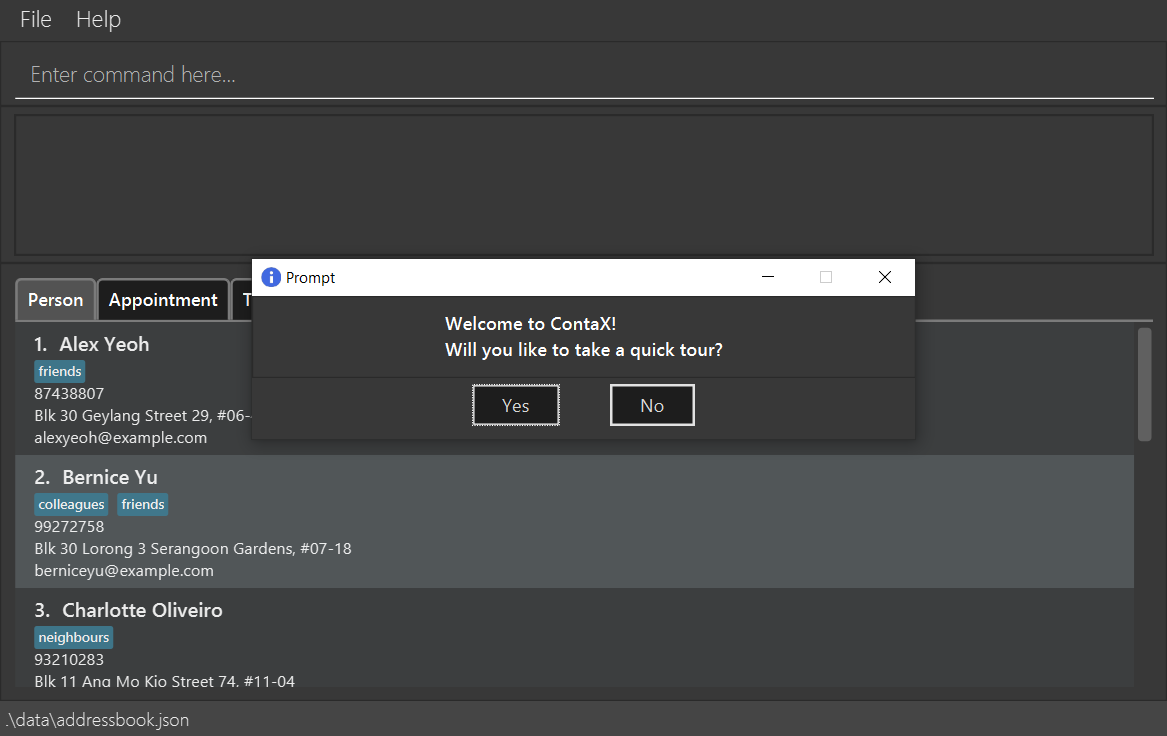
Prompt on first run
When you run the program for the first time, you will be prompted to take a quick tour of the ContaX’s basic functions guided through a series of step-by-step instructions. You will be taken to the onboarding guide window if you select yes. If you choose no, the prompt will just close.
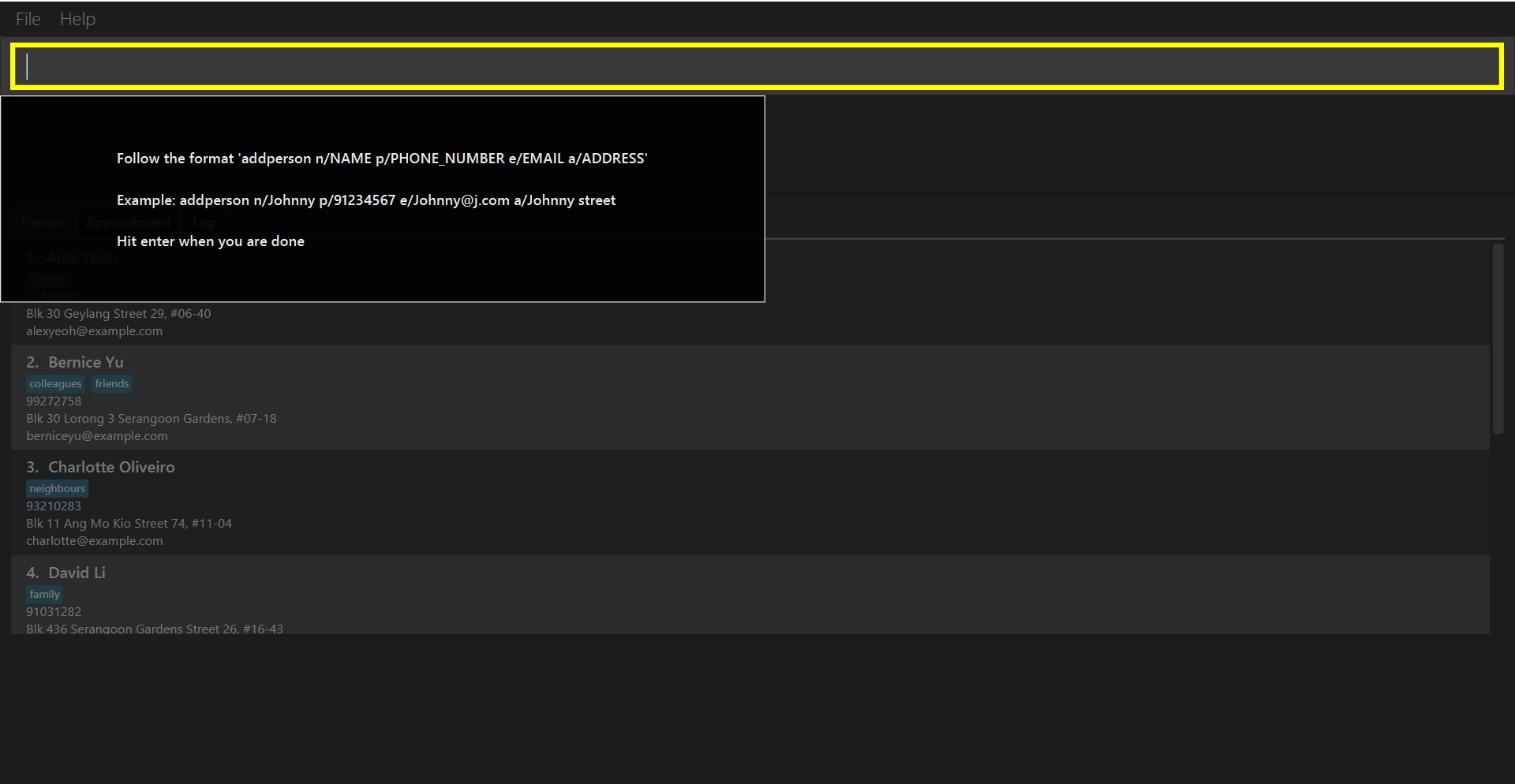
When going through the onboarding guide, instructions such as the one shown below will be displayed, and important areas will be highlighted.
Basic features covered The onboarding guide will cover the following:
- Add person
- Find person
- Delete person
- List persons
![]() Important Note: The order and case-sensitivity of keywords for
Important Note: The order and case-sensitivity of keywords for findperson is only fixed for the Onboarding Guide.
Viewing help : help
Shows the commands available and the syntax for all of them. It also includes a link to this user guide for further reading.
Format: help
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all contacts and tags from the address book and all appointments from the schedule.
Format: clear
Adding a person: addperson
Adds a person to the address book.
Format: addperson n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]…
| Parameter | Constraints |
|---|---|
NAME |
Must not be blank, and contain only alphanumeric characters and spaces |
PHONE_NUMBER |
Must be at least 3 digits long. May optionally start with a country code E.g. 1234 and +6512345678 are both valid |
EMAIL |
Must follow the format local-part@domain.local-part must only contain alphanumeric characters and the symbols +_.-.domain is made up of 1 or more parts separated by periods, and must end with a part that is at least 2 characters long.E.g. john@piserver and john2@email.com are valid. |
ADDRESS |
No constraints |
TAG |
Must contain only alphanumeric characters and spaces |
Examples:
addperson n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01addperson n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/1234567 t/criminal
Listing all persons : listpersons
Shows a list of all persons in the address book.
Format: listpersons
Editing a person : editperson
Edits an existing person in the address book.
Format: editperson INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
- Edits the person at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the person will be removed i.e adding of tags is not cumulative.
- You can remove all the person’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it. - If the parameters are specified, they must conform to the following constraints:
| Parameter | Constraints |
|---|---|
NAME |
Must not be blank, and contain only alphanumeric characters and spaces |
PHONE_NUMBER |
Must be at least 3 digits long. May optionally start with a country code E.g. 1234 and +6512345678 are both valid |
EMAIL |
Must follow the format local-part@domain.local-part must only contain alphanumeric characters and the symbols +_.-.domain is made up of 1 or more parts separated by periods, and must end with a part that is at least 2 characters long.E.g. john@piserver and john2@email.com are valid. |
ADDRESS |
No constraints |
TAG |
Must contain only alphanumeric characters and spaces |
Examples:
-
editperson 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st person to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
editperson 2 n/Betsy Crower t/Edits the name of the 2nd person to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
Locating persons by attribute: findperson
Finds persons whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: findperson KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] [by/SEARCH_TYPE]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans - Persons matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang - The
SEARCH_TYPEdetermines the attribute being searched, and must match one of the following:NameAddressPhoneEmail
- If
SEARCH_TYPEis not specified, default search type is byName.
Examples:
-
findperson JohnreturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
findperson Garden by/addresslists all persons whose address contain the keyword “Garden” -
findperson 87438807 by/phonelists all persons whose phone number matches “87438807” -
findperson alex davidreturnsAlex Yeoh,David Li
Deleting a person : deleteperson
Deletes the specified person from the address book.
Format: deleteperson INDEX
- Deletes the person at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
listpersonsfollowed bydeleteperson 2deletes the 2nd person in the address book. -
findperson Betsyfollowed bydeleteperson 1deletes the 1st person in the results of thefindpersoncommand.
Creating a Tag : addtag
Creates a new tag in ContaX.
Format: addtag n/TAGNAME
- The
TAGNAMEparameter must be specified, and can only contain alphanumeric characters and whitespaces. - If the
TAGNAMEalready exists (case-insensitive), the tag will not be created. - All tag names will be converted to lowercase characters.
Examples:
-
addtag n/Potential ClientsCreates a tag named potential clients in the address book (if it does not exist).
Editing a Tag : edittag
Edits an existing tag in ContaX.
Format: edittag INDEX t/NEW_TAGNAME
- All parameters must be specified.
- The
INDEXparameter must be a positive integer, and refers to the index number shown in the displayed tag list. - Changes the name of a tag at
INDEXtoNEW_TAGNAME. - An error will be thrown if either
INDEXis invalid orNEW_TAGNAMEalready exists in ContaX. - An error will be thrown if the tag at
INDEXhas the same name asNEW_TAGNAME
Examples:
-
edittag 1 t/Prospective ClientsChanges the name of first tag in the list to Prospective Clients.
Listing All Tags : listtags
Shows a list of all tags in ContaX.
Format: listtags
Example output
Deleting a Tag : deletetag
Deletes the specified tag in ContaX.
Format: deletetag INDEX
- The
INDEXparameter must be a positive integer, and refers to the index number shown in the displayed tag list. - When the tag is deleted, contacts that contain this tag will have the tag removed.
Examples:
-
deletetag 1Deletes the first tag in the tag list and disassociates any contacts that contain the specified tag.
Finding Contacts by Tag : findbytag
Finds persons whose tags match the given keyword.
Format: findbytag t/TAGNAME
- The
TAGNAMEparameter must be specified. - Search is case-insensitive e.g.
clientsis the same asClients. - If there are no tags that contain that keyword, an empty list will be displayed.
Examples:
-
findbytag t/friendsDisplays the contact information of contacts who have the friends tag.
Creating an Appointment : addappt
Creates an Appointment in the Schedule with the specified parameters.
Format: addappt n/NAME d/DATE t/TIME l/DURATION [p/PERSON]
- All parameters except
PERSONmust be specified.
| Parameter | Description | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
NAME |
The appointment’s name | Must be non-empty, and can only contain alphanumeric characters, spaces and the symbols .,!@#$%&*()-_=+
|
DATE |
The appointment’s starting date | Must conform to the Common Date Formats |
TIME |
The appointment’s starting time | Must conform to the Common Time Formats |
DURATION |
The appointment’s duration in minutes | Must be a positive integer |
PERSON |
A person associated with the appointment | If specified, must be a positive integer, and refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list |
Examples:
-
addappt n/Bi-Weekly Meeting d/14-02-2022 t/11:00 l/60Creates a one-hour appointment named “Bi-Weekly Meeting” on 14th Feb 2022 at 11:00 AM, associated with nobody in the contact list. -
addappt n/Contract Signing With Charlie d/22-10-2022 t/16:30 p/1 l/300Creates a 5-hour appointment named “Contract Signing With Charlie” on 22nd Oct 2022 at 4:30 PM, associated with the first person in the contact list.
Listing All Appointments : listappt
Shows a list of all Appointments in the Schedule.
Format: listappt
Example output
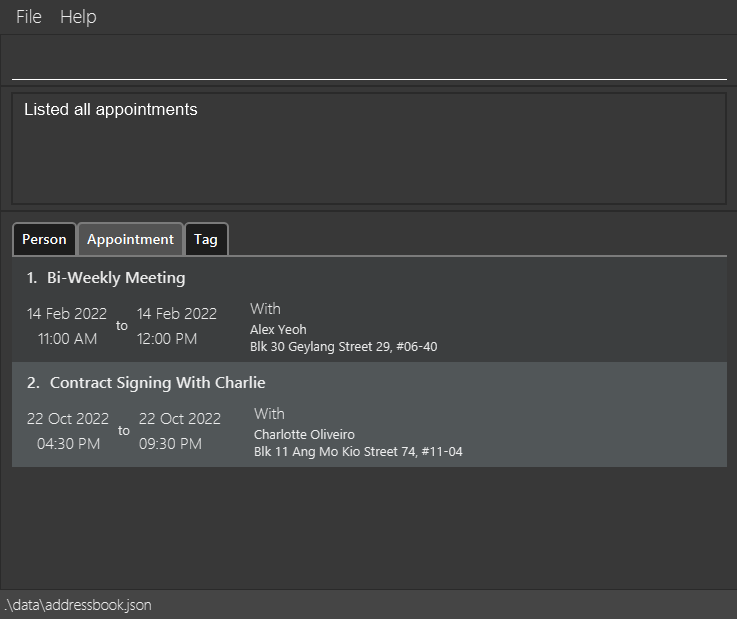
Deleting an Appointment : deleteappt
Deletes an Appointment previously created in the Schedule.
Format: deleteappt INDEX
- Deletes the appointment that is at
INDEXin the displayed appointment list. -
INDEXmust be a positive integer, and refers to the index number shown in the displayed appointment list.
Examples:
-
deleteappt 2Deletes the second appointment in the list of appointments.
Editing an Appointment : editappt
Edits an Appointment previously created in the Schedule.
Format: editappt INDEX [n/NAME] [d/DATE] [t/TIME] [l/DURATION] [p/PERSON]
- Edits the appointment that is at
INDEXin the displayed appointment list, setting the supplied parameter(s) to the supplied value(s). - The
INDEXparameter must be a positive integer, and refers to the index number shown in the displayed appointment list. - At least one of the optional parameters must be supplied, otherwise the command will be ignored.
- If supplied, the optional parameters must conform to the following rules:
| Parameter | Description | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
NAME |
The appointment’s name | Must be non-empty, and can only contain alphanumeric characters, spaces and the symbols .,!@#$%&*()-_=+
|
DATE |
The appointment’s starting date | Must conform to the Common Date Formats |
TIME |
The appointment’s starting time | Must conform to the Common Time Formats |
DURATION |
The appointment’s duration in minutes | Must be a positive integer |
PERSON |
A person associated with the appointment | Must be a positive integer or the String none.If a positive integer is provided, it refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list. The String none is used to dissociate the person associated to the appointment. |
Examples:
-
editappt 6 l/300 p/noneEdits the 6th appointment in the list of appointments to have a duration of 5 hours, and removes the person associated with the appointment. No other properties are changed. -
editappt 2 n/Call Juliet t/13:45 p/1Edits the second appointment in the list of appointments to have the name “Call Juliet”, changes the time to 1:45 PM and associates the appointment to the first person in the displayed persons list. No other properties are changed.
Listing Appointments Within A Period : apptbetween
Lists all appointments from a starting time to an ending time inclusive of both ends of the range. It will list all appointments that contain any sub-range of the provided period.
Format: apptbetween [sd/STARTDATE] [st/STARTTIME] [ed/ENDDATE [et/ENDTIME]]
ENDTIME is specified, then ENDDATE must be specified.
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
STARTDATE |
The starting date of the period | Today |
STARTTIME |
The starting time on the starting date for the period | 00:00 |
ENDDATE |
The ending date of the period | No upper limit |
ENDTIME |
The ending time on the ending date for the period | 23:59 |
- The start of the period must be before or equals to the end of the period.
- All specified parameters must conform to the Common Date and Time Formats.
Example:
-
apptbetween sd/21-10-2022 st/12:00 ed/23-10-2022 et/17:00Lists all appointments from 21 October 2022, 12 PM to 23 October 2022, 5PM. -
apptbetween st/08:00Lists all appointments from 8AM Today.
Example Output:
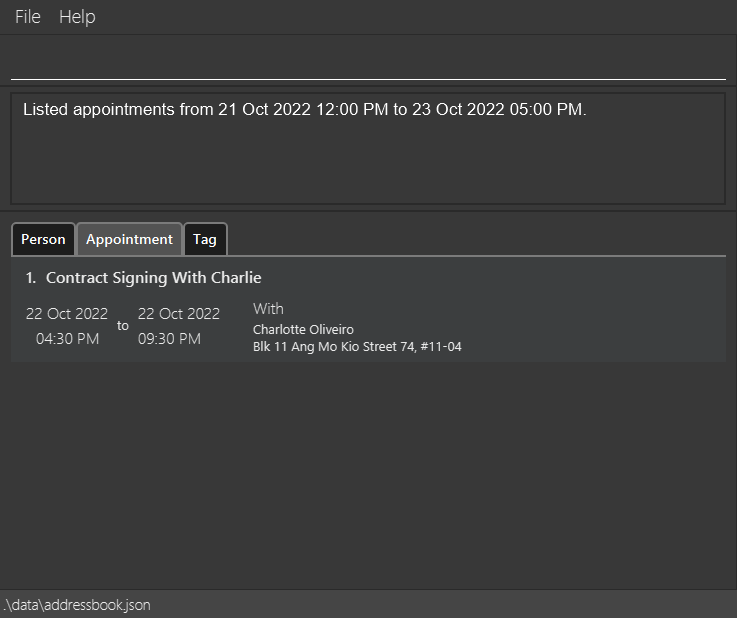
Listing Empty Slots in Schedule Within A Period : freebetween
Lists all empty slots in the schedule of a certain minimum duration, within the specified starting time to ending time. An appointment of the specified minimum duration can be inserted into each of the listed slots without causing any overlapping appointments in the schedule.
Format: freebetween l/DURATION [sd/STARTDATE] [st/STARTTIME] [ed/ENDDATE [et/ENDTIME]]
ENDTIME is specified, then ENDDATE must be specified.
| Parameter | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
STARTDATE |
The starting date of the period | Today |
STARTTIME |
The starting time on the starting date for the period | 00:00 |
ENDDATE |
The ending date of the period | No upper limit |
ENDTIME |
The ending time on the ending date for the period | 23:59 |
DURATION |
the minimum duration of the slots listed in minutes. It must be a positive integer |
Required Field |
- The start of the period must be before or equals to the end of the period.
- If any of
STARTDATE,STARTTIME,ENDDATEorENDTIMEare specified, they must conform to the Common Date and Time Formats.
Example:
-
freebetween sd/21-10-2022 st/12:00 ed/23-10-2022 et/17:00 l/60Lists all empty slots in the schedule that are at least 60 minutes (1 hour) long between 21 October 2022, 12 PM and 23 October 2022, 5PM. -
freebetween st/09:30 l/20Lists all empty slots in the schedule that are at least 20 minutes long from 9:30AM today.
Example Output:
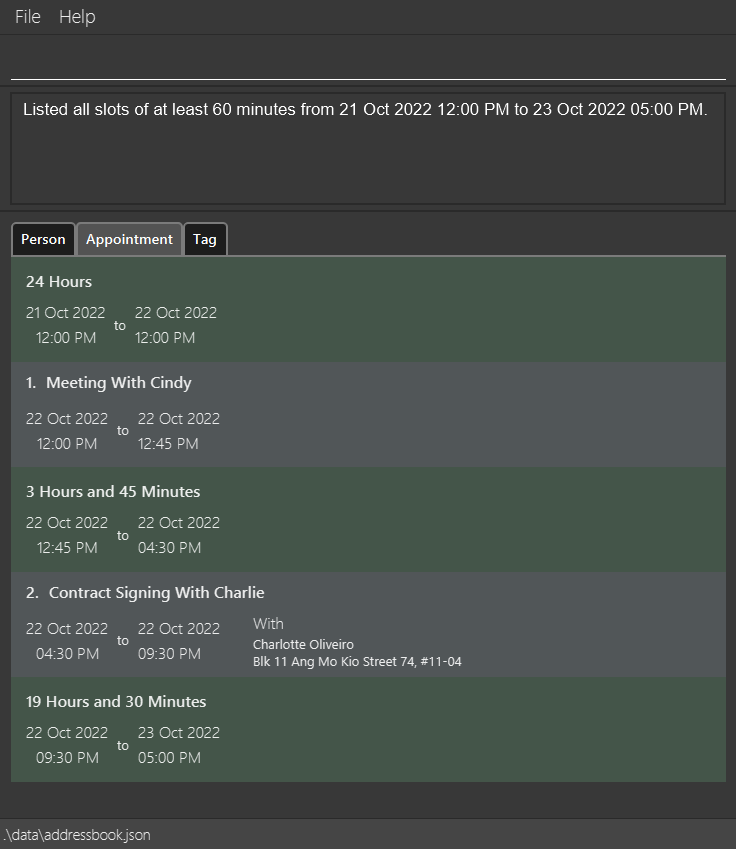
Edit Priority Level of an Appointment : prioritizeappt
Edits priority level of an Appointment previously created in the Schedule.
Format: prioritizeappt INDEX pri/PRIORITY
- Edits the priority of appointment that is at
INDEXin the displayed appointment list, setting the priority to the supplied value. - The
INDEXparameter must be a positive integer, and refers to the index number shown in the displayed appointment list. - The
PRIORITYparameter must not be same as existing priority level for appointment atINDEXin the displayed appointment list. - The
PRIORITYparameter must be non-empty, and can only contain below values (case-insensitive):- High
- Medium
- Low
- None
Examples:
-
prioritizeappt 6 pri/highEdits the 6th appointment priority level in the list of appointments to have a status of high. -
prioritizeappt 2 pri/noneRemoves the second appointment priority and set status to none.
Example Output:
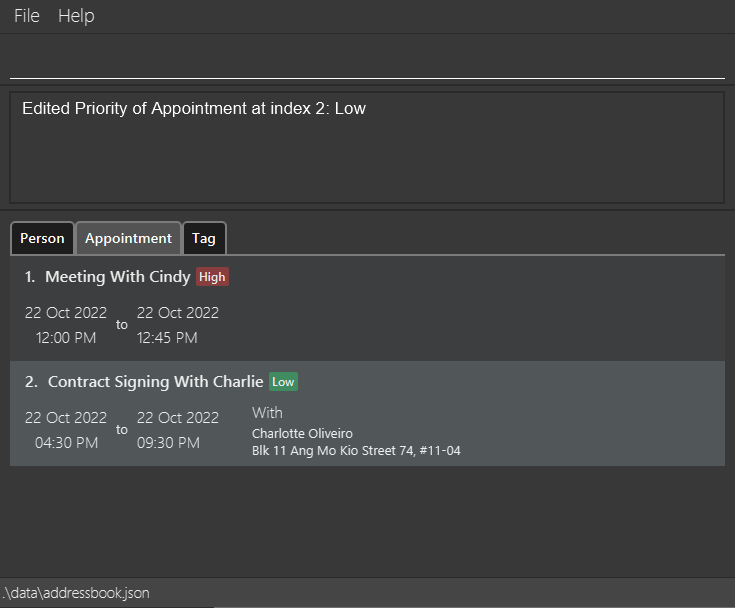
Finding Appointment by Name or Person Name : findappt
Finds appointments with name or Person name that contains the given keyword.
Format: findappt KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] [by/(person OR name)]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
Meetingwill matchmeeting - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Meeting Herewill matchHere Meeting - Only full words will be matched e.g.
Meetingwill not matchMeetings - Appointments matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Meeting Herewill returnMeeting There,Meeting Now - If
by/personis included, the appointments will be matched based on the person name. - If
by/nameis included, the appointments will be matched based on the appointment name. - If neither
by/namenorby/personare specified, the appointments will to default to match based on the appointment name.
Example:
-
findappt MeetingLists all appointments with name that containsMeeting. -
findappt Johnny by/personLists all appointments with person name that containsJohnny.
Saving the data
ContaX contact data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes contact data in JSON format at [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json.
Appointment data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes appointment data in JSON format at [JAR file location]/data/schedule.json.
Exporting the data: exportcsv
Exports the current list of contacts as a CSV file that can be imported through ContaX or viewed separately via Microsoft Excel
ContaX formatted CSV files are as follows:
- First row contains headers delimited by commas. Headers used are
Name,Phone,Email,Address,Tagged - Second row onwards will contain contact information corresponding to the column headers.
An example exported CSV file is as follows. This can be opened by text editors or spreadsheet management applications like Microsoft Excel.
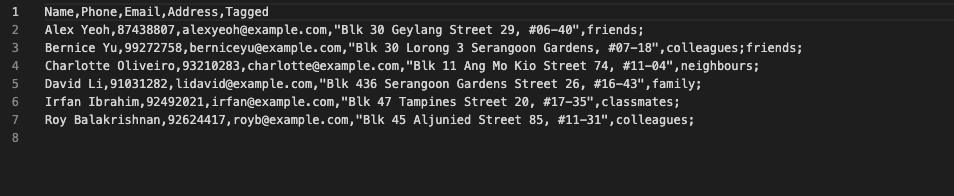
Format: exportcsv
- Exports CSV as per ContaX format. This file can be imported by other instances of ContaX.
- File will be saved on the directory
[JAR file location]/data/addressbook.csv
Examples:
-
exportcsv: Exports the current address book as a CSV file at[JAR file location]/data/addressbook.csv
Editing the data file
ContaX contacts and appointments data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes contact data in JSON format at [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json and [JAR file location]/data/schedule.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Importing data
In order to import data from external sources into ContaX, there are the following options:
- Replacing
addressbook.jsonorschedule.jsonfile with a valid ContaX formatted generated by another system with ContaX - Importing CSV Files
Importing CSV Files: importcsv
Format: importcsv f/FILEPATH [n/COLUMN_NAME] [p/COLUMN_PHONE] [e/COLUMN_EMAIL] [a/COLUMN_ADDRESS] [t/COLUMN_TAGS]
- Imported contacts will be appended to the current address book.
- Each argument represents the corresponding attribute for a person.
-
COLUMN_NAME- specifies column number for Name -
COLUMN_PHONE- specifies column number for Phone -
COLUMN_EMAIL- specifies column number for Email -
COLUMN_ADDRESS- specifies column number for Address -
COLUMN_TAGS- specifies column number for Tags
-
- If any argument is omitted, it will follow the next available column based on the default sequence of Name - Phone - Email - Address - Tags
- Fields should comply with existing field restrictions, e.g. no alphabets in Phone.
- Tags should be in the delimited by
;e.g.tag1;tag2;tag3;, in the imported CSV file. - If the specified rows clash, the command will fail.
- If there are lines with illegal characters or invalid formatting, ContaX will skip importing the affected line
- This is designed with flexibility in mind, such that users will be able to export CSV files from any other format and do minimal data organisation before importing into ContaX
Examples:
-
importcsv f/file.csv n/2 p/3 e/5 a/6 t/4- Reads from a CSV file treating the 2nd column as names, 3rd column as phone numbers, 5th column as email addresses, 4th column as tags.
-
importcsv f/file.csv n/2- Reads from CSV treating the 2nd column as names, 3rd column as phone numbers, 4th column as email addresses, 5th column as tags.
-
importcsv f/file.csv- Reads from CSV with default ContaX format positions
Operate on Contacts by Conditional Clause : batch
Performs operations on contacts in the address book that match the given condition.
Format: batch COMMAND by/FIELD [=/EQUALS_VALUE] [start/START_WITH] [end/END_WITH]
-
COMMANDmust be a valid command withoutINDEX. The allowed operations inCOMMANDare:- edit
- delete
- The
FIELDprovided must be provided, and must match one of the following:NameAddressPhoneEmail
- Exactly one parameter of
EQUALS_VALUE,START_WITH, orEND_WITHmust be provided. - A
EQUALS_VALUEis value matching the exact value in the target field.- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans.
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
- A
START_WITHis value matching the value in the target field with specific starting value. - A
END_WITHis value matching the value in the target field with specific ending value.
Examples:
-
batch deleteperson by/name start/A- Deletes all persons whose name start with A (case-sensitive)
-
batch editperson p/87438806 by/phone =/87438807- Edit contact with phone matches keyword 87438807 change to 87438806
batch operation is transactional, either all changes succeed or all changes fail (should an operation within batch fails). Any error message shown is from the failing operation.
Operate on Contacts within Range : range
Perform actions on a group of contacts.
Format: range COMMAND from/INDEX_FROM to/INDEX_TO
- Performs the specified
COMMANDon all contacts between the specified range ofINDEX_FROMtoINDEX_TOinclusive. -
COMMANDmust be a valid command withoutINDEX. The allowed operations inCOMMANDare:- edit
- delete
- The
INDEX_FROMandINDEX_TOparameters must be positive integers, and refer to the index number shown in the displayed person list. -
INDEX_FROMmust be less thanINDEX_TOsupplied, otherwise the command will fail. - The resultant effect of the command is dependent on the performed action.
Examples:
-
range editperson e/johndoe@example.com from/6 to/10- Sets the email address of the 6th to 10th contacts in the address book to
johndoe@example.com.
- Sets the email address of the 6th to 10th contacts in the address book to
-
range deleteperson from/2 to/3- Deletes the 2nd and 3rd contacts in the address book.
range operation is transactional, either all changes succeed or all changes fail (should an operation within range fails). Any error message shown is from the failing operation.
Chaining Commands: chain
Perform multiple actions in a single command.
Format: chain COMMAND_A && COMMAND_B [&& COMMAND_C ...]
- Calls multiple specified commands.
- A valid command (i.e. The syntax of
COMMANDmust be correct) must be supplied before and after the&&operator, otherwise the command will fail
Examples:
-
chain editappt 6 l/360 && listappt- Edits the 6th appointment in the list of appointments to have a duration of 6 hours. Then list all appointments in the Schedule
-
chain deleteappt 2 && addappt n/Contract Signing With Charlie d/22-10-2022 t/16:30 p/1 l/300- Deletes the 2nd appointment in the list of appointments.
- Then, create a 5-hour appointment named “Contract Signing With Charlie” on 22nd Oct 2022 at 4:30 PM, associated with the first person in the contact list
chain operation is executed sequentially, it will execute the commands from left to right until a given command fails. Any error message shown is from the failing operation, and all preceding operations will be saved.
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous AddressBook home folder.
addressbook.json and schedule.json, both of which need to be copied for a complete transfer of all saved data.
Q: Can I edit the data manually?
A: Yes, simply open addressbook.json to edit Contacts and schedule.json to edit Appointments. Note that if you change a Contact’s name in addressbook.json, you will also need to change it in schedule.json.
Q: Why is ALL my data missing?
A: Your data file is probably corrupted (likely in the JSON structure). Do not enter any command, close the application, and fix your data file!
Q: Why is some of my data missing?
A: There is probably some invalid information in your data file. Invalid records are discarded during loading, and those records you do not see might be invalid. Do not enter any command, close the application, and fix your data file!
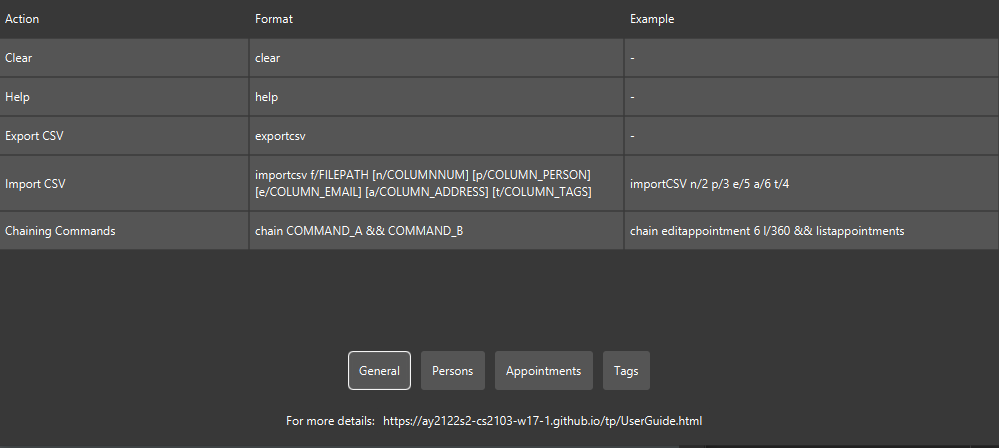
Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Add Person |
addperson n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]… e.g., addperson n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/friend t/colleague
|
| Clear | clear |
| Delete Person |
deleteperson INDEXe.g., deleteperson 3
|
| Edit Person |
editperson INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…e.g., editperson 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com
|
| Find Person |
findperson KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] [by/SEARCH_TYPE]e.g., findperson James Jake by/name
|
| List Persons | listpersons |
| Add Tag |
addtag n/TAGNAME e.g., addtag n/Potential Clients
|
| Edit Tag |
edittag INDEX t/NEW_TAGNAME e.g., edittag 1 t/Prospective Clients
|
| List Tags | listtags |
| Delete Tag |
deletetag INDEX e.g., deletetag 1
|
| Find Contacts By Tag |
findbytag t/TAGNAME e.g., findbytag t/friends
|
| Add Appointment |
addappt n/NAME d/DATE t/TIME l/DURATION p/PERSONe.g., addappt n/Call Bob d/14-02-2022 t/11:00 p/2 l/60
|
| List Appointments | listappt |
| Delete Appointment |
deleteappt INDEXe.g., deleteappt 2
|
| Edit Appointment |
editappt INDEX [n/NAME] [d/DATE] [t/TIME] [p/PERSON] [l/DURATION]e.g., editappt 2 n/Call Juliet t/13:45
|
| List Appointments Within Period |
apptbetween [sd/STARTDATE] [st/STARTTIME] [ed/ENDDATE [et/ENDTIME]] e.g. apptbetween sd/21-10-2022 st/12:00 ed/23-10-2022 et/17:00
|
| List Available Slots Within Period |
freebetween l/DURATION [sd/STARTDATE] [st/STARTTIME] [ed/ENDDATE [et/ENDTIME]] e.g. freebetween sd/21-10-2022 st/12:00 ed/23-10-2022 et/17:00 l/60
|
| Find Appointment |
findappt KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] [by/(person OR name)] e.g findappt Meeting
|
| Help | help |
| Export CSV | exportcsv |
| Import CSV |
importcsv f/FILEPATH [n/COLUMNNUM] [p/COLUMN_PERSON] [e/COLUMN_EMAIL] [a/COLUMN_ADDRESS] [t/COLUMN_TAGS] e.g., importCSV n/2 p/3 e/5 a/6 t/4
|
| Operate on Contacts by Conditional Clause |
batch COMMAND where/CONDITION e.g., batch editperson p/87438806 by/phone =/87438807
|
| Operate on Contacts within Range |
range COMMAND from/INDEX to/INDEX e.g., range editperson e/johndoe@example.com from/6 to/10
|
| Chaining Commands |
chain COMMAND_A && COMMAND_B e.g., chain editappt 6 l/360 && listappt
|